What is a Depth Tester and How Does it Work in Different Applications
In various industrial applications, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of measurements is critical for operational success. A depth tester emerges as an invaluable tool in this context, providing precise depth measurements for materials such as metals, plastics, and coatings. According to a recent market analysis report by Industry Research, the global depth measurement devices market is expected to reach $7.5 billion by 2025, reflecting a growing demand driven by advancements in manufacturing and quality assurance processes. This underscores the significance of depth testers in maintaining the standards required in highly regulated sectors, such as aerospace and automotive engineering.
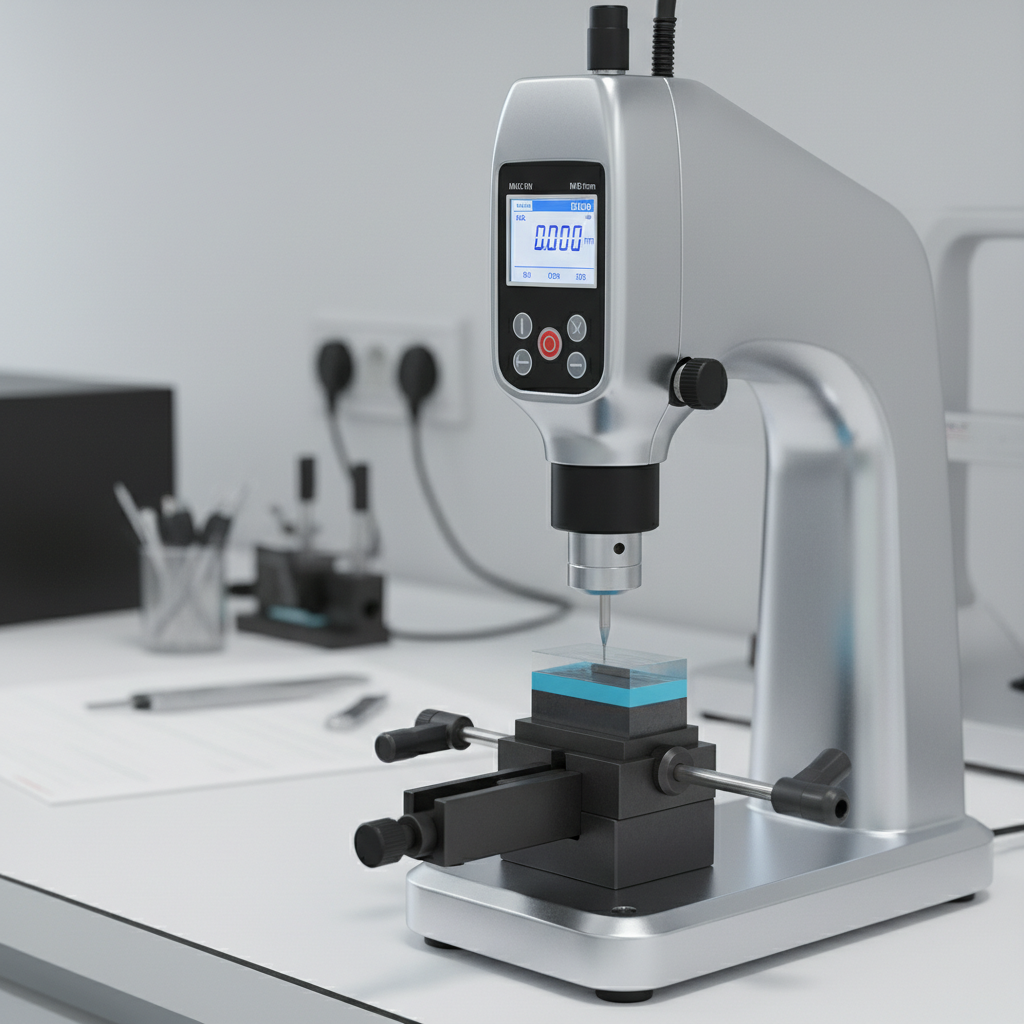

Depth testers operate on a simple yet effective principle: utilizing a measuring probe to assess the depth of indentations, holes, or coatings. Their functionality is paramount in applications ranging from automotive component assessment to the aerospace industry, where even minute deviations can lead to critical failures. The versatility of depth testers, combined with the increasing complexity of products, further emphasizes their role in enhancing quality control measures. With data indicating that manufacturers who implement depth testing can improve product quality by up to 30%, it is clear that these tools are essential in achieving consistent compliance with industry standards and customer expectations.
What is a Depth Tester?
A depth tester is a precision measuring tool used to determine the depth of holes, grooves, or recesses in various materials. It typically consists of a base, a measuring rod or shaft, and a dial gauge or digital display. These instruments are widely employed in industries such as manufacturing, construction, and quality control, where accurate depth measurements are critical. According to a report by Market Research Future, the global depth measurement tools market is projected to grow by 5.3% annually, reflecting the increasing need for precise engineering applications.
In practical use, depth testers are particularly valuable in machining operations, where they help ensure the correct depth of drilled holes or cutouts, directly influencing product quality and safety. They are also essential in automotive manufacturing to verify component fit and assembly, contributing to the sector's stringent standards. Furthermore, advancements in technology have led to the development of digital depth testers that offer enhanced accuracy and functionality, making them indispensable in modern engineering workflows.
Key Components of a Depth Tester
A depth tester is an essential tool in various industries, primarily used for measuring and verifying the depth of holes or features in components. Understanding its key components is crucial for optimal performance in applications such as machining, automotive, and construction. The primary components of a depth tester include the measuring probe, the depth rod, and the dial gauge or digital readout. The measuring probe is designed to engage with the surface of the material, while the depth rod extends down into the hole. The dial gauge or digital readout displays accurate measurements, often with a precision of 0.01 mm, ensuring reliability in critical applications.
For instance, a recent report from the Manufacturing Technology Association highlighted that integrating advanced depth testers can enhance accuracy by up to 30% in precision machining tasks. This improvement directly translates to better quality control and reduced material waste, making the investment in reliable depth testing technology a worthwhile consideration for manufacturers.
Tips for using a depth tester effectively include ensuring the device is calibrated regularly to maintain accuracy and always cleaning the measuring probe before use to avoid contamination. Additionally, it is beneficial to perform test measurements in a controlled environment to reduce variables that can impact the readings. Maintaining these best practices can significantly enhance the takeaways from using a depth tester across various applications.
How Depth Testers Function in Various Applications

Depth testers are versatile instruments used across various industries to measure the depth of holes, slots, and grooves. Their design allows for accurate readings, which are crucial in applications like manufacturing, construction, and quality control. In manufacturing, for instance, depth testers ensure that components meet specified tolerances, preventing costly errors in assembly and enhancing the overall reliability of the products. The ability to measure depth with precision supports efficient production processes while ensuring adherence to safety standards.
In the automotive sector, depth testers play a key role in evaluating brake and suspension components. By measuring the depth of grooves and slots, engineers can ascertain their effectiveness and make necessary adjustments to optimize vehicle performance. Similarly, in construction, depth testers are employed to assess the depth of foundation excavations or drainage installations, ensuring structural integrity and compliance with regulatory requirements. The ability to apply depth testing across these various applications highlights its significance in promoting safety and efficiency in modern industry.
Advantages of Using Depth Testers in Industry
Depth testers are essential tools in various industries, providing precise measurements that ensure quality and safety in manufacturing processes. One of the primary advantages of using depth testers is their ability to enhance product accuracy. By measuring the depth of features such as holes or slots, manufacturers can confirm that components comply with design specifications, reducing the likelihood of defects that could arise from improperly sized parts. This accuracy not only streamlines production but also minimizes waste, thereby improving overall operational efficiency.
Additionally, depth testers improve time management in production environments. Modern digital depth testers allow for quick data capture and analysis, enabling operators to make immediate adjustments if discrepancies are detected. This capability contributes to faster turnaround times and the ability to maintain consistent quality across large production runs. Furthermore, implementing depth testers as a part of routine quality control procedures can lead to higher customer satisfaction, as clients receive products that meet their exact specifications every time, ensuring reliability and trust in the manufacturing process.
Common Industries Utilizing Depth Testing Technology
Depth testing technology is increasingly utilized across various industries to ensure precision and quality control in products and processes. In the manufacturing sector, depth testers play a crucial role in assessing the integrity of components, particularly in automotive and aerospace applications. According to the 2025 AI Index Report, the integration of artificial intelligence in depth testing has enhanced accuracy and efficiency, enabling manufacturers to detect flaws that could compromise safety.
Moreover, the healthcare industry is leveraging depth testing technology for applications such as non-destructive testing of medical devices and implants. As the demand for high-quality healthcare products rises, depth testing ensures that these devices meet strict regulatory standards. The advancements in generative AI not only contribute to improved testing methods but also promise substantial economic value, projected to add trillions to the global economy.
The construction industry also benefits significantly from depth testing technology, particularly for ensuring the stability and safety of structures. Accurate depth measurements influence project outcomes, reducing the risk of costly failures. Reports indicate that the global semiconductor industry's growth, projected to surge in 2025, will further increase demand for precise testing solutions in various applications, including depth testing.
Related Posts
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Quality Testing Equipment for Your Business
-

Understanding the Essential Role of Field Test Equipment in Modern Industries
-

Water Testing Meter Innovations and Market Trends at the 138th Canton Fair in 2025
-

Maximize Your Game: How a Ball Rebound Tester Can Enhance Your Basketball Skills
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Phone Testing Equipment for Your Needs
-

Revolutionizing Quality Control: The Impact of Testing Meters in Modern Manufacturing Industries