How to Conduct Steel Testing: Methods, Standards, and Best Practices
Steel testing is an essential process in the material science field, serving as a cornerstone for ensuring the quality and integrity of steel products used across various industries. With the growing emphasis on safety and performance, understanding how to conduct effective steel testing has become paramount. This article endeavors to explore the methods, standards, and best practices that are vital for conducting thorough and reproducible steel testing.
The methods of steel testing range from non-destructive techniques, such as ultrasonic testing and magnetic particle inspection, to destructive methods like tensile and impact testing. Each method serves specific purposes and adheres to recognized standards that ensure equivalency and reliability. By examining these methods in detail, readers will gain insights into how to select the appropriate testing procedure based on the type of steel and its intended application.
Furthermore, adherence to established standards is crucial in maintaining consistency and accuracy in steel testing. Various organizations have developed guidelines that facilitate the testing process, providing benchmarks for quality and safety. Incorporating these best practices not only enhances the testing process but also contributes to the overall performance of steel components in real-world applications. Through this discussion, we aim to equip engineers, manufacturers, and quality control professionals with the knowledge necessary to conduct steel testing effectively and responsibly.

Introduction to Steel Testing: Importance and Applications
Steel testing plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and performance of steel products in various applications, ranging from construction to manufacturing. Industry standards, such as those set by ASTM and ISO, stipulate specific testing methods that gauge properties like tensile strength, ductility, and fracture toughness. These properties are essential for predicting how steel will behave under different loads and environmental conditions. According to a report by the World Steel Association, nearly 1.9 billion metric tons of steel were produced globally in 2020, which underscores the need for rigorous testing to maintain structural integrity and quality in this vast industry.
The importance of steel testing extends beyond quality control; it’s pivotal in regulatory compliance and risk management. For instance, structural steel must meet the requirements outlined in building codes to prevent failures that could result in catastrophic consequences. A study published in the Journal of Constructional Steel Research indicates that buildings designed with properly tested steel can enhance safety and longevity, reducing the risk of costly repairs or safety hazards. By adhering to established testing protocols, industries can not only comply with legal obligations but also advance innovation in steel applications, ensuring that new materials and designs can withstand evolving challenges in construction and manufacturing.
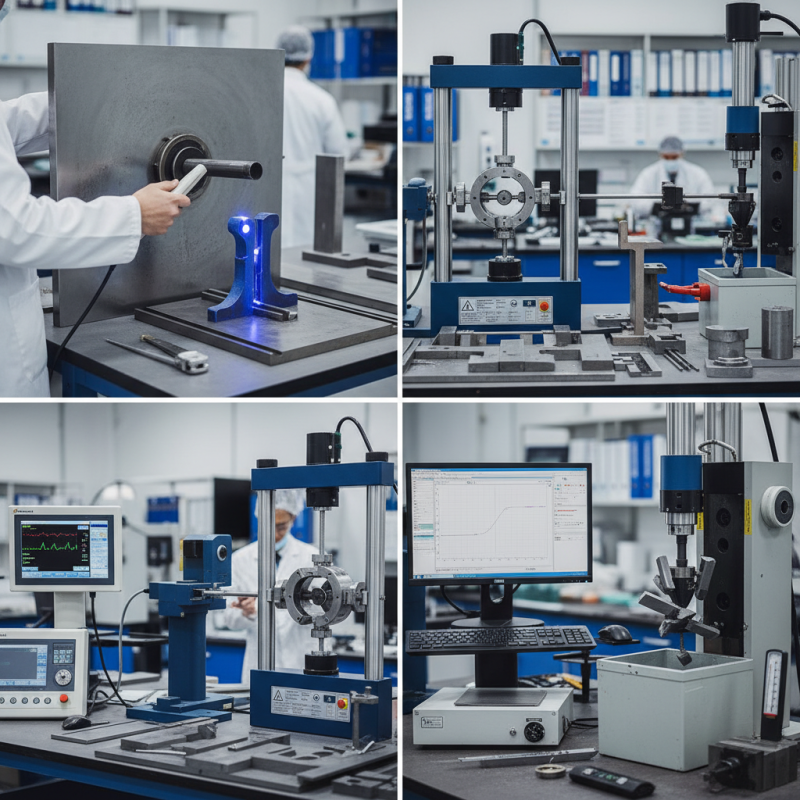
Key Methods for Steel Testing: Overview and Description
Steel testing is a critical process that ensures the material meets specific performance criteria and safety standards. Among the key methods for steel testing, tensile testing is one of the most widely used techniques. This method measures the strength and ductility of steel by stretching a sample until it breaks. According to the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), tensile testing can provide valuable data such as yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, and elongation, which are crucial for applications ranging from construction to automotive manufacturing.
Another important method is hardness testing, which evaluates the material's resistance to deformation. The Rockwell and Brinell tests are prominent hardness evaluation techniques in the industry. Reports from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) indicate that hardness metrics directly correlate with wear resistance and overall durability, making these tests vital for predicting the longevity of steel products in various environments. In the field, these tests often complement each other; for instance, a combination of tensile and hardness testing helps manufacturers ensure that their steel meets both strength and wear requirements, aligning with industry standards for safety and performance.
Steel Testing Methods Overview
Standards and Specifications for Steel Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to steel testing, adherence to established standards and specifications is crucial for ensuring the material's reliability and performance. Various organizations, such as ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and ISO (International Organization for Standardization), have developed comprehensive guidelines that outline methods for evaluating steel properties. These standards dictate the testing procedures, equipment required, and criteria for pass or fail results. By following these guidelines, manufacturers and quality control personnel can maintain consistency and accuracy in their testing processes, leading to safer and more reliable steel products.
In addition to standardized testing methods, it's important to understand the specifications that pertain to the specific types of steel being tested. These specifications detail the required mechanical properties, such as tensile strength, yield strength, and elongation, as well as any necessary chemical composition. By referencing these specifications during the testing process, engineers can ensure that the steel meets the necessary performance parameters for its intended application. Furthermore, familiarity with updated standards helps professionals stay compliant with industry regulations, enhance product quality, and mitigate risks associated with material failure.
Best Practices for Conducting Accurate Steel Tests and Measurements
When conducting steel tests, precision and adherence to best practices are crucial for achieving accurate and reliable results. To ensure that your testing aligns with industry standards, proper preparation and a thorough understanding of the testing methods are essential. Prioritize the calibration of your testing equipment before commencing any tests. This will help eliminate any discrepancies that may affect your measurements and results.
Tips for accurate steel testing include maintaining a controlled environment during testing. Fluctuations in temperature or humidity can influence the properties of the steel being tested. Additionally, ensure that the steel samples are free of contamination, as impurities can distort the outcomes. Finally, document each step of the testing process meticulously, including the settings of the equipment and environmental conditions, to ensure reproducibility.
Consistency in sample preparation is also vital. Follow a standardized procedure to cut, grind, and polish samples, as inconsistencies can lead to variations in results. Implementing a system for regular training and certification of personnel involved in the testing process can further enhance accuracy. By focusing on these best practices, you can achieve reliable results that contribute to the overall quality assessment of steel materials.
How to Conduct Steel Testing: Methods, Standards, and Best Practices
| Test Method | Standards | Purpose | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Test | ASTM E8 | Determine yield and tensile strength | Calibrate machines regularly; use standardized specimens |
| Hardness Test | ASTM E18 | Assess material hardness | Ensure surface preparation; apply consistent load |
| Impact Test | ASTM E23 | Evaluate toughness of material | Use proper specimens; calibrate drop weight |
| Chemical Composition Analysis | ASTM E415 | Determine alloy content and impurities | Maintain clean sample environment; validate calibration |
| Ultrasonic Testing | ASTM E317 | Detect internal flaws | Optimize transducer frequency; follow proper scanning method |
Interpreting Steel Test Results: Quality Assurance and Analysis Techniques

Interpreting steel test results is crucial for ensuring quality assurance in manufacturing processes. Understanding the various metrics from tests such as tensile strength, yield strength, and ductility allows engineers to evaluate whether a specific steel type meets industry standards. Analyzing these results requires a keen eye to spot anomalies and assess the consistency of steel properties, which directly impacts its performance in real-world applications. This process often involves comparing results against established standards such as ASTM or ISO, ensuring that any deviation is addressed before moving forward with production.
Tips: When reviewing steel test results, always start by familiarizing yourself with the relevant standards that apply to your specific project. This will help you set the benchmark for acceptable performance. Additionally, utilize statistical analysis methods, such as control charts, to identify trends over time. This approach not only helps in spotting potential quality issues early but also contributes to continuous improvement in your manufacturing processes.
Another important aspect of interpreting steel test results is collaboration. Engaging with metallurgists and quality assurance experts can provide valuable insights into material behavior and test implications. By discussing findings as a team, you can ensure a comprehensive evaluation of the results, leading to better decision-making and adherence to safety regulations. Regular communication within the team can further enhance understanding and foster a culture of quality awareness.
Related Posts
-

What is Meter Test Equipment? A Complete Guide to Understanding Its Importance and Usage
-

Innovative Solutions for Precision Line Testers
-

Maximizing Efficiency with Field Test Equipment Advantages for Your Business
-

Understanding the Essential Role of Field Test Equipment in Modern Industries
-

Understanding the Importance of Impact Tester in Modern Manufacturing Processes
-

Water Testing Meter Innovations and Market Trends at the 138th Canton Fair in 2025